The Role of Hearing Care Professionals in Rehabilitation
When hearing difficulties start affecting your conversations at work,


When hearing difficulties start affecting your conversations at work,

At the start of a new year, many people focus on their health by
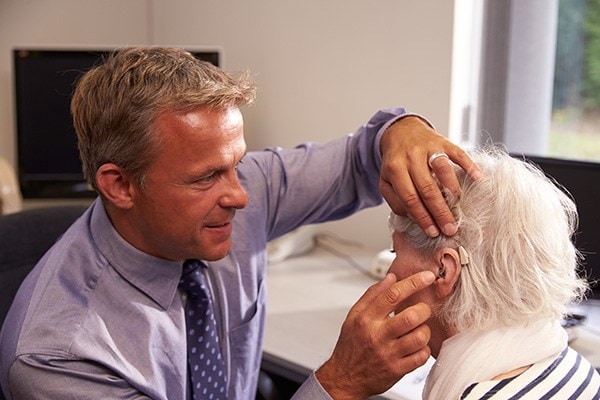
Ever been in the middle of a conversation when suddenly your hearing aid